The decision on the type of treatment to be applied is a gradual process.In essence it begins once certain symptoms or signs causing suspicion
that there is cancer and progresses through the diagnostic process.Once the diagnosis is made, after a positive biopsy, several factors are taken into account:
The stage
The most critical factor is the extent of filtered area around the tumor. Sometimes it is not possible to assess the stage before the surgeon see the volume. But there are other ways, other than surgery, to reveal what stage the
volume (imaging methods such as ultrasound, CT and MRI, etc.).
In staging should be investigated many other areas of the body for any evidence of cancer being. The various tests will reveal the extent of dispersion and possible infection of other tissues. Therefore you need different tests, eg blood to determine the functionality of various organs, for example kidney and liver.
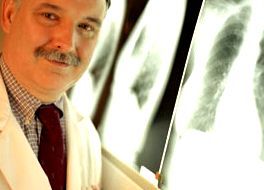
Imaging techniques such as radiographs or chest CT and MRI scans are
used to determine whether the lungs are affected, either directly or by
metastases.
Depending on the primary site and the tumor type, would be several more specific tests. Each tumor type has its own dispersion. So we need to explore different anatomical regions of the body, depending on each case.
Prostate cancer, for example, often metastasizes to bone. Therefore the most appropriate tests for metastasis control is scintigraphy, the bone radiographs and other blood tests. Lung
cancer can be dispersed to the center of the chest (mediastinum) region
mapped CT or MRI or directly controlled by endoscope
(mesothorakoskopio). The stomach and bowel cancers commonly spread to the liver, so we need
computed tomography, scintigraphy liver and haematological and
biochemical tests to confirm the dispersion.
It is important to understand that when a cancer metastases grants, the type remains the same as the original. Breast cancer which metastasizes to bone is not converted to bone cancer. If dispersed in the lungs is not lung cancer.
Wherever installed, he will grow as breast cancer. More simply, like the seeds of dandelion which scatter with the wind blowing. Where the seed falls, in the field, in the forest or on the sidewalk, will sprout again dandelion. This point is important because the treatment depends mainly on where
the tumor starts (ie from primary site) and not from where you come.
The biology of the disease
Analysis of disease-cell type, biology and expected symperifora- is necessary. Tumour biology plays an important role in the treatment of which can slow down or even stop disease progression.
Current alternatives
When
completed the staging process, the physician should consider all
appropriate therapies depending on the type of tumor, the primary site
and stage of dispersion. In some cases a single special treatment is generally accepted as the most appropriate. Most often, however, other approximation methods may be used.
The cancer treatments are constantly evolving. Every year new discoveries are made and old methods or amended or repealed. But it is difficult even for specialists to learn about all the latest developments in this field. However, there are many ways to determine the primary physician of
the patient the most modern treatment methods are considered as the
last word of science:
At this stage the physician consulted by specialists oncologists, surgeons and specialists aktinotherapefton.
Studying the latest literature, eg by means of an electronic
computer which has specific information for each type of cancer
programs.
Doctors and specialists oncologists monitor many of the numerous
oncology conferences that take place every year and presented
interesting results of investigations and given other information about
cancer.
oncology boards
Another way to obtain more information the doctor or to exchange views
on the best ways of treatment, especially when it comes to unusual
types of cancer, is to participate in so-called oncological councils.
Such councils exist in all hospitals where there is treatment of
oncological cases, offer an opportunity for the specialist cancer
doctors to discuss specific cases and to exchange views on the
advantages and disadvantages of different treatment methods.
also
customary to discuss the results of biopsies presented and explained by
pathologists and radiologists and specialists in nuclear medicine have
radiographs and scans. The
attending physician of the patient or the oncologist will expose
(anonymously) the incident and so each member council will have at his
disposal the same information with the patient's doctor to decide on the
treatment. So when he asked the doctor to recommend treatment, will collect the opinions of a large group of experts.
individual factors
Benefits and risks. The
type of treatment will ultimately be chosen depends on several
individual factors such as age, other medical problems (which may render
dangerous surgery), and particularly the possibility of severe side
effects from one or the other treatment. Age plays an important role when choosing the type of treatment
because a patient forty years easily tolerate an aggressive chemotherapy
which can bring substantial remission.
But
if we grant the same dosage to a patient eighty years may be dangerous,
because at that age the kidneys are not working as well as the younger,
so the risk of treatment may exceed the potential advantages. Each case, therefore, must also be examined separately. Doctor and patient must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each
regimen, the expected degree of remission or cure the disease and the
possible side effects and ultimately decide together.
The final decision
A good discussion of the patient with the doctor is valuable for the final decision. The physician must be able to explain the staging process, the trials and their results, as well as all existing therapies. Appropriate, make any information collected in oncology councils where the case was discussed.
It also can convey the outcome of informal talks that are usually made in group gatherings physicians dealing with cancer. It should also be aware of alternative forms of treatment and suggest
solutions if the cancer does not respond to initial treatment or a
problem occurs.
So
the final decision on the selection of case better treatment option is
the result of mature data processing from both sides (therapeutic team
and patient), always with the best interests of the latter
No comments:
Post a Comment